Hearing a lot about heat pumps but feeling a bit lost?
In this blog, we break down the questions on many people’s minds, including What is a heat pump? How do heat pumps work? We’ll also outline some of their key benefits to help you understand if a heat pump is right for you.
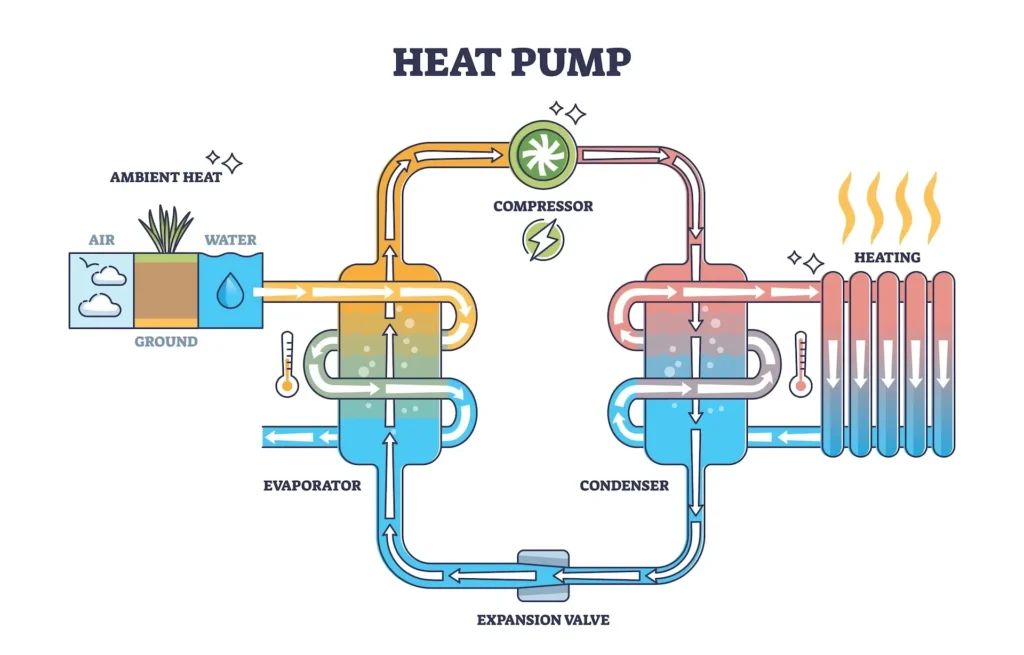
How Do Heat Pumps Work?
Heat pumps are an innovative way to heat and cool your home efficiently. Heat pumps work by transferring thermal energy from one location to another using a refrigeration cycle. A simple way to explain heat pumps is that they work the same way as a fridge, but in reverse.
Heating Mode
- Heat Extraction: The heat pump draws low grade thermal energy from an external source, such as outdoor air, the ground, or a water body. Even in cold weather, these sources contain usable heat.
- Evaporation: The refrigerant absorbs this heat as it evaporates at low pressure.
- Compression: The vaporised refrigerant is compressed, significantly increasing its temperature.
- Heat Release: The now hot refrigerant releases its heat indoors as it condenses, effectively warming the indoor space.
Cooling Mode
In cooling mode, the cycle is reversed:
- Heat Extraction: The heat pump extracts heat from the indoor air and transfers it outside.
- Evaporation: The refrigerant absorbs indoor heat as it evaporates.
- Compression: It is then compressed to a higher temperature and pressure.
- Heat Release: Then, heat is released to the outdoors during condensation.
Types of Heat Pumps
There are several types of heat pumps, each transferring heat in different ways. We know this can be confusing, so we’ve broken down the main types and how they work below.
- Air Source Heat Pumps: pulls heat from the outside air.
- Ground Source (Geothermal) Heat Pumps: extracts heat from the ground.
- Water Source Heat Pumps: use a nearby water source.
- Hybrid Systems: combine heat pumps with traditional heating for backup.
Inside a Heat Pump: Key Components & Their Roles
Heat pumps have several key components that are needed to help them run and transfer heat.
Here is a breakdown of the key components and what they are used for:
- Evaporator coil – absorbs heat
- Compressor – pressurises refrigerant
- Condenser coil – releases heat
- Expansion valve – controls refrigerant flow
- Reversing valve – switches heating/cooling modes
Why Are Heat Pumps Efficient?
Heat pumps offer a highly efficient method of heating by transferring heat rather than generating it, resulting in significantly lower energy consumption compared to boilers. As well as their superior efficiency, heat pumps typically have lower operational costs, making them a cost effective long term investment. They are also a sustainable heating solution that can substantially reduce your property’s carbon emissions, which will have a positive environmental impact.
How Efficient Are Air Source Heat Pumps in Winter?
A common concern for homeowners considering air source heat pumps is their effectiveness during the winter months. The good news is that air source heat pumps are designed to work efficiently even in cold weather. In fact, modern systems can still extract heat from the air at temperatures as low as -15°C, although their efficiency does reduce slightly as the temperature drops.
That said, air source heat pumps work best in homes that are well-insulated. Good insulation helps to retain the heat generated, ensuring that your system doesn’t have to work as hard to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. If your home has poor insulation, you may need to improve it before installing a heat pump, which could add to the initial costs.
Best Time of Year for Installation
The ideal time for installing a heat pump depends on various factors:
- Milder Weather Conditions: Installing a heat pump during milder weather, typically in spring or early autumn, can be advantageous. The ground is more accessible for GSHP, and the moderate temperatures make the installation process smoother.
- Off-Peak Seasons: Scheduling your installation during less busy times for heating professionals, such as late spring or early summer, often means quicker service and potentially lower costs.
- Preparation For Winter: Having your heat pump installed before the onset of winter ensures that your home will be warm and comfortable when the colder weather arrives.
Ensuring Your Heat Pump Lasts
Typically, heat pumps are designed to last for 15-20 years with proper maintenance. Regular heat pump servicing improves the efficiency and lifespan of your unit. Servicing also identifies issues early on before they lead to more serious problems that need expensive repairs.
Between services, you should clean your unit’s filters regularly to avoid them becoming clogged and causing issues.
Where Do Heat Pumps Work Best?
Currently, heat pump efficiency varies depending on insulation and heating system design.
Modern heat pumps are ideal for residential properties, small businesses, and retrofit projects. Thanks to recent advancements, they also perform well in cold climates, making them an efficient, reliable option year round.
They are most effective in buildings with good insulation and efficient heat distribution systems. Their performance relies heavily on a building’s ability to retain heat, which is why well insulated homes tend to see the greatest benefits. For optimal performance and energy savings, ensuring the building is properly insulated is key. This not only boosts efficiency but also helps maximise the lifespan and value of the heat pump system.
Heat Pump Installation
Heat pump installation is a process that takes two to five days to complete. It involves preparing the area, as usually heat pumps are installed on the ground at the back or side of a building. Then the outdoor unit is installed and connected to the indoor components. In some cases a heat pump installation can include upgrading existing heating systems and radiators.
At Premium Heating Plumbing & Cooling we are Heat Geek Elite certified heat pump installers. Our status shows that we have undergone thorough training in heat pump installation, it proves that we have extensive knowledge of these heating systems and the skills needed to provide our customers with a heat pump installation service they can trust.
Understanding the Costs: Upfront Investment vs Long Term Savings
While heat pumps typically have a higher upfront cost compared to traditional HVAC systems, they offer significant long-term value through improved energy efficiency. A substantial part of this investment can be claimed back through the government’s ‘Boiler Upgrade Scheme’ (BUS) scheme which entitles you to claim £7,500 towards the cost of your heat pump installation to encourage the adoption of sustainable heating. Over time, the energy savings provided by a heat pump can lead to noticeably lower utility bills, making it a smart financial choice for homeowners looking to reduce their long term heating costs.
Overall, heat pumps are a highly efficient and environmentally friendly heating solution. Instead of generating heat like a boiler, they transfer it, requiring much less energy. This makes them cheaper to run over time, with the added benefit of significantly lowering your home’s carbon footprint.
Join the future of heating.
